News
-
Blimp-1 is a crucial gatekeeper in epidermal immunity
Blimp-1 is a transcriptional repressor, that is, a protein which can inhibit the expression of genes; it has been demonstrated to be a significant player in the immune system.
-
Collaborated Translational Research Tracks Down FUT8 in Lung Cancer
With a persistent quest and clever collaborations, digging clue after clue, a team in Dr. Chi-Huey Wong’s research group has identified the role of FUT8, an enzyme which adds sugar molecules to proteins; their study showed FUT8 matters a LOT in human nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
-
Location Matters
DNA methylation is already a known key factor that attributes to the gene expression, namely, its presence has a direct correlation between regarding gene being “turned on” or not, therefore, it has become quite a marker for epigenetic study.
-
A Breakthrough in Carbohydrate-Based Vaccine: One Vaccine Targets Three Unique glycan Epitopes on Cancer Cells and Cancer Stem Cells
A cure for breast cancer may be in sight! The GRC research team has been studying carbohydrate antigens on the surface of cancer cells and cancer stem cells for years. Lately, a published paper on PNAS reports their new finding of some special carbohydrates.
-
Strike on the Drug Resistance Problems of Influenza Infections
Tamiflu, an orally available drug targeting influenza neuraminidase, has been used widely in clinics for treating influenza virus infections. Over the years of usage, influenza viruses have developed resistance over Tamiflu.
-
Negatively Charged Gold Nanoparticles Proved to Ease the Accumulation of Proteins Causing Alzheimer’s Disease
A new gold rush in the biotech world has been underway, studies of gold particles in nano scales have been applied to researches from cancer treatments to bio-imaging technologies. Now, a collaborated study led by Dr. Ruby Chen may have just added another possible application to this precious metal that we humans treasure from way back.
-
A Brave New Way to Tackle the Hepatitis C Viral Problem
By pushing the boundaries and thinking out of the box, Dr. Tien-Hsien Chang demonstrates once again what a scientific spirit is all about.
-
Lin’s Lab Unravels the Pathway of Plasma Cells
There are millions variations of B cells, and when a certain type of B cells are called on duty, their mission is to make specific plasma cells, which act as sole purpose factories focusing on making a specific type of antibodies.
-
Potential Dengue Fever Treating Antibody - Proved Effective for Japanese Encephalitis Viral Infections
CLEC5A is a C-type lectin expressed on the cell surface known to be a receptor which is used by the Dengue virus (DV) to attach themselves to of the host cells during infection. It also induces massive proinflammatory cytokines subsequently in an infected host. The blocking of the CLEC5A interaction with DV has been one of the research interests in Dr. Shie-Liang Hsieh’s group.
-
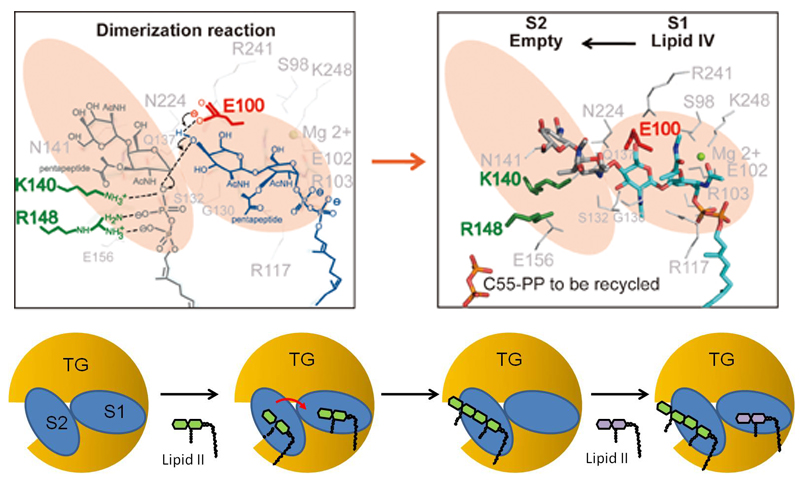
Last Piece of the Bacterial Transglycosylase Puzzle Solved
Peptidoglycan is a major component of the bacterial cell wall and essential for bacteria to survive. Bacterial transpeptidase and transglycosylase on the cell surface are the two key enzymes responsible for making peptidoglycan.
-
Specific Glycosphingolipids identified for Differentiation Precursors of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
In the pursuit of surface glycosphingolipids (GSLs) markers during the lineage-specific differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), the team led by Dr. John Yu has made another major discovery of specific GSLs associated with differentiations of early embryonic cells toward specific progenitors of neural or endodermal cell types.
-
Genomics Research Center Team Succeeds in Oligosialic Acid Synthesis, Brings Totally Synthetic Antibacterial Vaccine One Step Closer
Polysialic acids are useful in the development of antibacterial vaccines because they can be conjugated (joined) to a carrier protein as a vaccine to be administered to humans to induce a bactericidal effect. Up until now the polysaccharides used in vaccines have been isolated from pathogenic bacteria, but due to the difficulty in purification, vaccines may consist of polysaccharides of various lengths and possibly be contaminated with other antigenic components.
-
Insights into Broadly Protective Vaccination Against Influenza
Yearly, as the temperature goes down, it is inevitable to hear about flu shots, for it has already become a seasonal event for the sake of getting protections from the flu.
-
Not One, Not Two, But, Eight! Hung and Chang Make the Octasaccharides That Can Inhibit Type 1 Herpes
When it comes to solving the living problems, biologists and chemists usually team up to analyze and recreate. After all, all nature’s creations can be broken down into molecules and chemical elements.
-
Highlighting the Highlights
Several GRC research papers published in 2010 and reported on the A-IMBN website were further included in the “Research Highlights Collection 2010”. The complete version of this collection is available from the A-IMBN website.
-
New Hopes to Conquer Drug-resistant Problem by Green Chemistry
To save lives, man develops antibiotics to kill bad bugs, which otherwise foster super bugs to emerge. To fight back the invincible super bugs by developing more effective antibiotics sounds paradoxical, but it is a fate, a never ending story.
-
Chang’s Anti-CεmX Invention Transferred to New Drug Development
Since it is rare that a technology transfer deal is reported by multiple press media, we hoped to get some insider scoops so that we could share them with other researchers. More than willingly, Professor Chang and his team agreed to spare some time with us.
-
Glycosphingolipid Profile on the Surface of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Identified
Combining the strengths in mass spectrometry analysis with stem cell technologies, an inter-disciplinary collaboration has unveiled a new way to pinpoint human embryonic stem cells. Scientists from Academia Sinica have identified a group of surface markers that can be used effectively in the study of embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) as well as cancer therapeutics.
-
A Chip That Tells More Sweet Findings
The fundamental mechanism of sugar chips is to design, make, and arrange various glycosylated molecules on a tiny glass chip, and then, by observing their binding with substance applied on the chip, one can find out the identity of the substance.
-
Yu’s Translational Medicine Journey of Neuroblastoma
Back in May 2009, when Dr.Alice Yu presented the results of the Phase III clinical trial of a noval antibody-based immunotherapy (chimeric anti-GD2 antibody ch14.18) for treating high-risk Neuroblastoma patients at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), it was listed as top 5 targeted therapy and received wide attention. The ch14.18 antibody immunotherapy is now made available to all eligible patients.