News
-
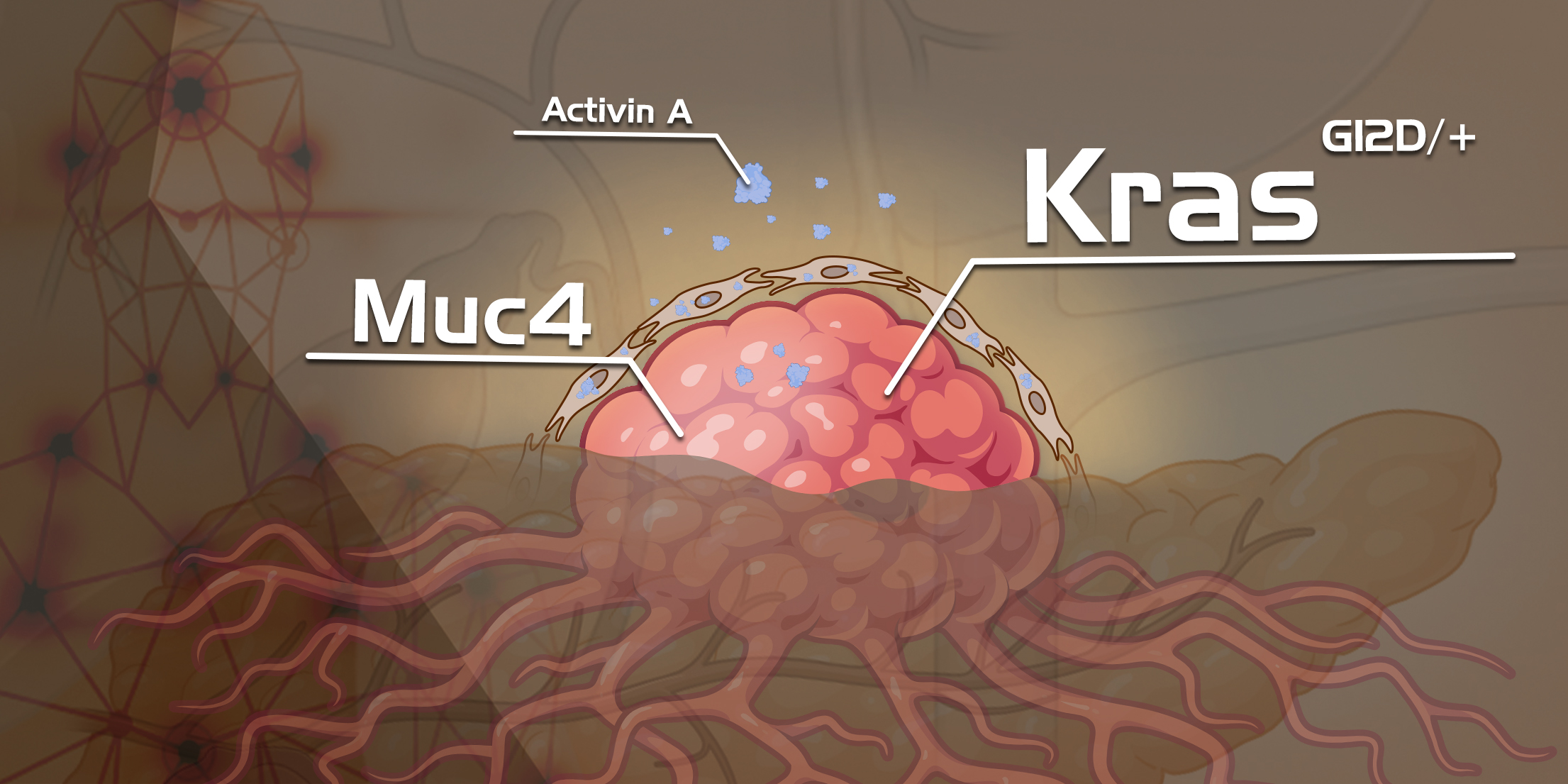
Unveiling the Mystery of Cancer-Causing KRAS Gene Driving Pancreatic Precancerous Lesions
As normal cells undergo abnormal proliferation, morphological changes, and eventually transform into cancer, there is a transitional phase known as "precancerous lesions" in pathology.
-
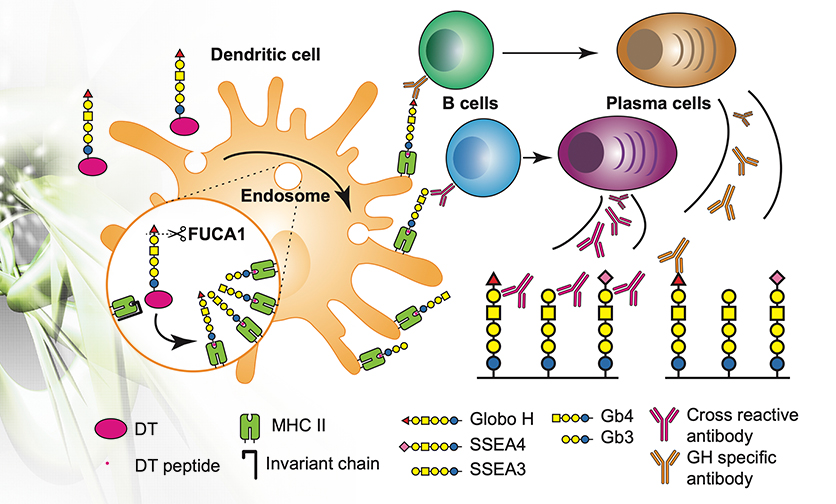
Unveiling Antigen Presentation and Cross-reactive Antibody Response of an Oligosaccharide-conjugate Vaccine, Paving the Way for Advanced Cancer Vaccines
Cancer has been a major threat to human health and the number one cause of death. In addition, the healthcare spending in cancer has been the largest among all diseases.
-
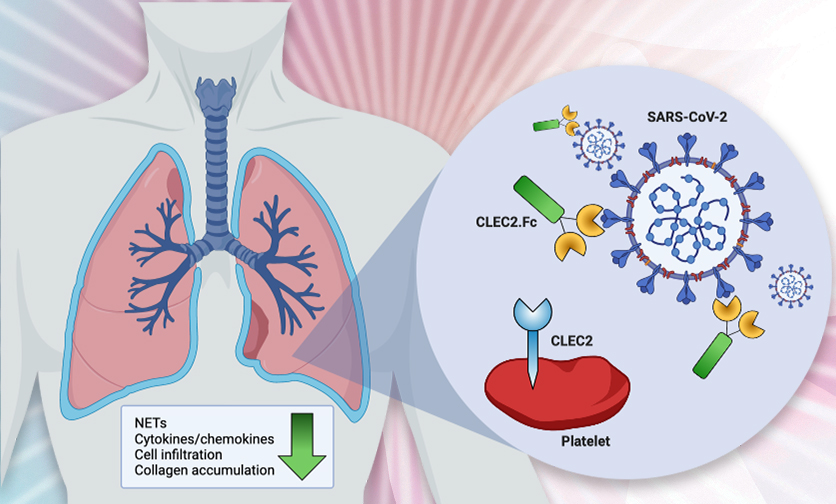
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2-mediated thromboinflammation by CLEC2.Fc
With the rampant spread of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) worldwide, it has caused severe inflammation and even death in COVID-19 patients.
-
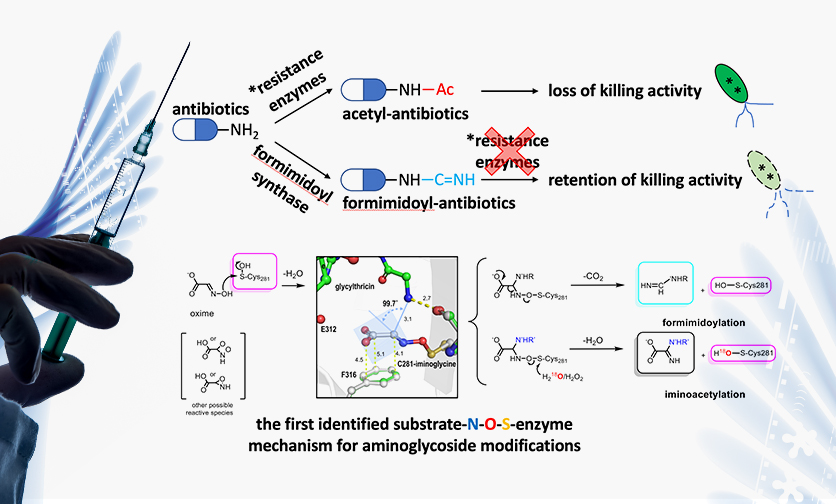
N-Formimidoylation/-iminoacetylation modification in aminoglycosides requires FAD-dependent and ligand-protein NOS bridge dual chemistry
Aminoglycoside antibiotics are essential drugs used in the clinical treatment of bacterial infections. These antibiotics work by binding to bacterial ribosomes, thereby inhibiting protein production.
-
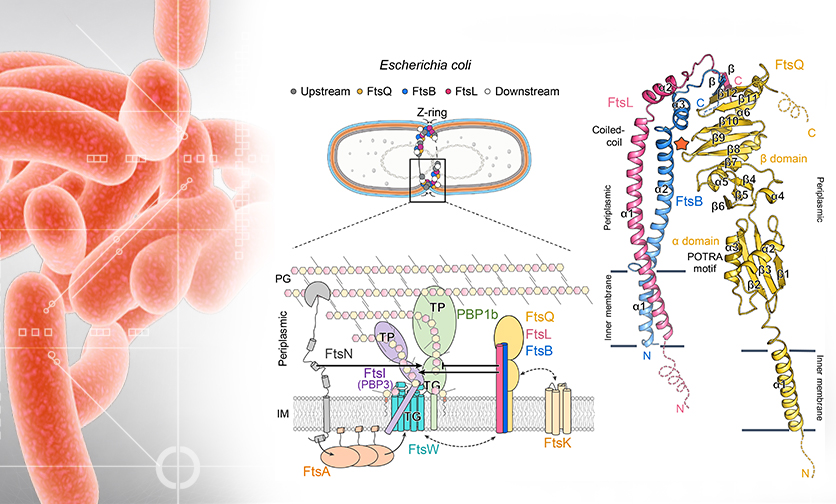
Structure of the heterotrimeric membrane protein complex FtsB-FtsL-FtsQ of the bacterial divisome
Among many strategies in pursuit of new antibiotics for treating resistant bacterial infections, one important approach is to identify and exploit novel targets for the development of new inhibitors.
-
Inducing PODXL overexpression breaks a new milestone in the efficiency of interspecies chimerism in 8-cell embryos
Considering factors such as human immune rejection, limited organ donations, and restrictions on their preservation methods, organ transplantation has been in a state of short supply globally.
-
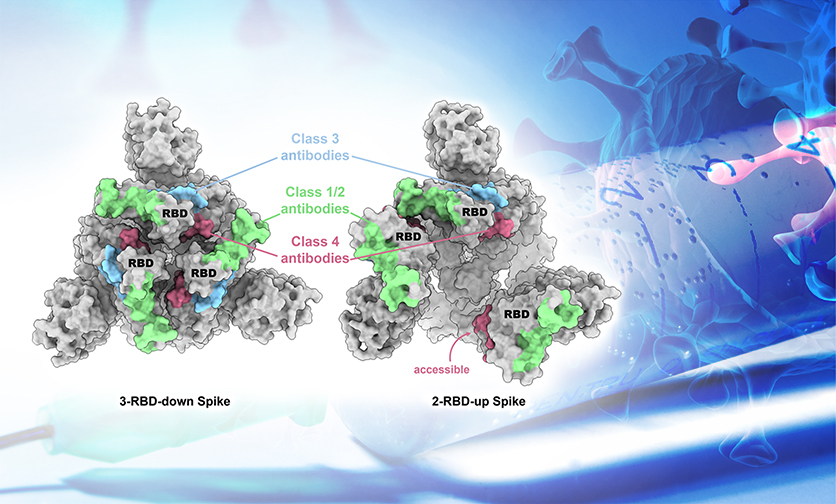
Structural basis for a conserved neutralization epitope on the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2
The COVID-19 pandemic seems to be fading away from our daily life, but the threat of a recurring circulation of new variants still haunts.
-
The circles Part II: investigating causal relationship between genetic variants and circular RNA expression in autism
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a pervasive neurodevelopmental and heritable complex disorder characterized by limited social communication, restricted and ritualized interests, and repetitive behavior [Mendelian Inheritance in Man (MIM) 209850].