News
-
PBP1b Research Rippled
Key Structure of Membrane Protein PBP1b Research Finding Published on PNAS back in May by GRC researchers had since drew attention and reported further by the elite journals including A-IBMN (Asia-Pacific International Molecular Biology Network), SciBX(Science-Business eXchange) and Scientific American Taiwanese edition.
-
Chen’s Study Shows Women with Hepatitis B Virus Infection Have Higher Risk with Liver Cancer
Risk for hepatocellular carcinoma, a primary malignancy of the liver, was statistically significantly higher among women with hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection than among women without the virus, according to a study published online June 17 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
-
Key Structure of Membrane Protein Unveiled For Finding Next Antibiotics
This is the first time ever the mechanism of the enzyme that holds the key to bacterial cell wall formation is disclosed in details. The PBP1b contains 4 domains required for the synthesis of bacterial cell wall: the transglycosidase domain (TG), the transpeptidase domain (TP), the transmembrane domain (TM), and a yet to be defined domain called UB2H.
-
Professor Alice Yu’s Pioneering Immunotherapy Proved Effective for Childhood Neuroblastoma In Phase III Trial
A new immunotherapy treatment pioneered by Dr. Alice Yu has resulted in an average 20% improvement in the rates of cure for children with neuroblastoma. This is the first effective immunotherapy reported for the disease and the first improvement on any neuroblastoma therapy cure-rates for 10 years.
-
Breast Cancer Related Researches Highlighted by A-IMBN RESEARCH
GRC research works on developing a breast cancer vaccine, and a method for early detection of breast cancer were both extracted and reported by the A-IBMN (Asia-Pacific International Molecular Biology Network) website, which is jointly produced by A-IMBN and NPG Nature Asia-Pacific, the Asia-Pacific wing of Nature Publishing Group.
-
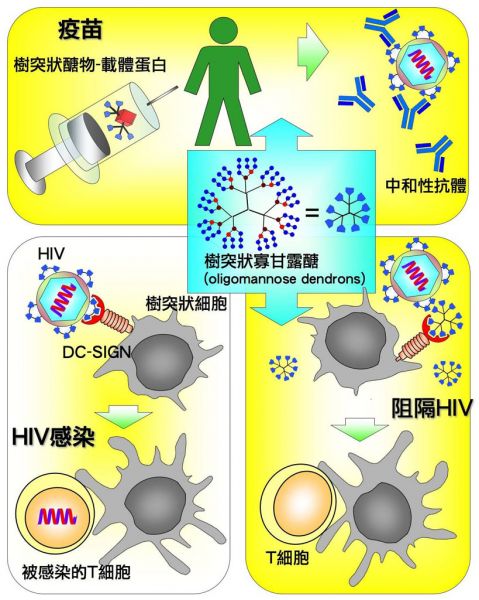
Genomics Research Center Awarded IAVI Grant for HIV Vaccine Research
The Genomics Research Center (GRC) was awarded a grant of total 19 million NT dollars over three years starting July 2008 from the International AIDS Vaccine Initiative (IAVI), an international not-for-profit foundation dedicated to AIDS Vaccine Development. IAVI focuses solely on the development of “safe, effective, accessible, preventive” vaccines for HIV, and supports AIDS research at key research institutes and universities around the world.
-
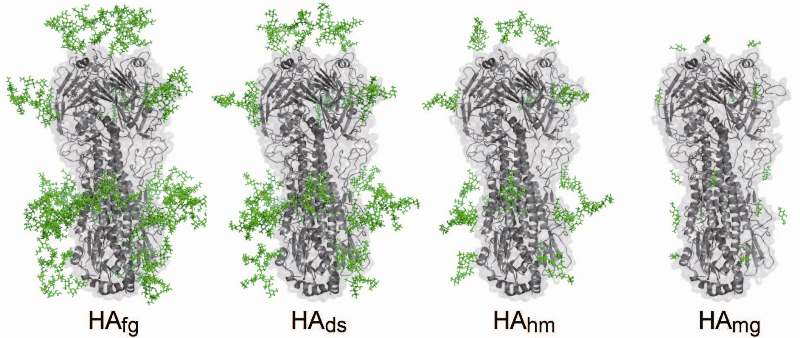
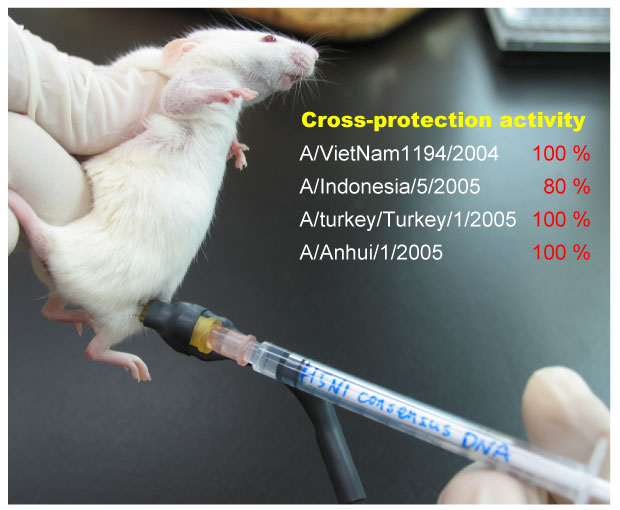
A Broadly Protective and Highly Effective H5N1 DNA Vaccine Developed
It is known that a type of glycoprotein molecule called Hemagglutinin (HA) found on the surface of the H5N1 virus is used by the virus to infect host cells in the first step of its attack.
-
Wong's Lab Achieves Breakthroughs in Glycoprotein Synthesis and Sugar Chip Development
Ninety percent of the proteins in our body are glycoprotein, which are proteins coated with all kinds of sugar molecules. It is known that all the antibodies are glycoproteins, and most of infections caused by virus and the spread of cancer are often involved in using a carbohydrate compound to interact with certain glycoprotein receptor.
-
Breast Cancer Vaccine Can Target Cancer Stem Cells
Frustrations in finding effective cures for cancer have led researchers looking into the cancer stem cells (CSCs) in recent years. CSCs possess the capability of stem cells to multiply and differentiate into their progenitors, display resistance to chemotherapy and radiation therapy, and could be the root cause for relapse and metastasis of cancerous tumors.
-
Hepatitis B Virus Genotype and Mutants Can Predict Risk of Liver Cancer
There are 400 million people worldwide, including 18% of adult population in Taiwan, are affected with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
-
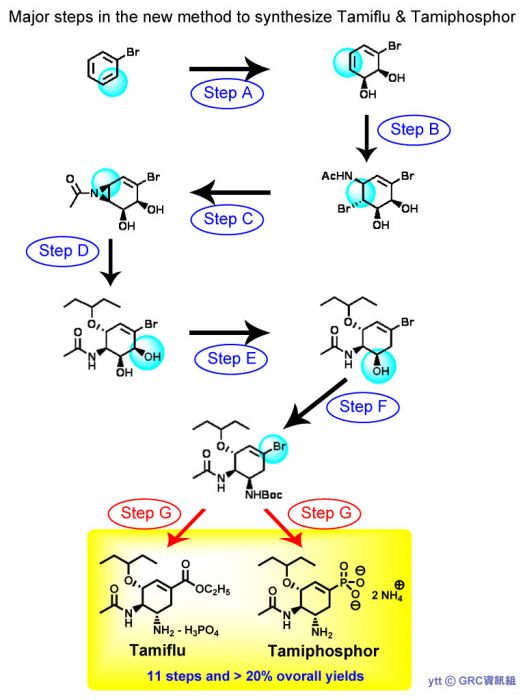
Novel Method for Synthesis of Tamiflu and Tamiphosphor Makes a Leap in Finding H5N1 Antagonist
Ever since the first highly pathogenic H5N1 virus was isolated in 1996, human cases of avian influenza have been reported throughout the world. Threats of avian flu were reported in Southeast China, Hongkong and Pakistan just this past month.
-
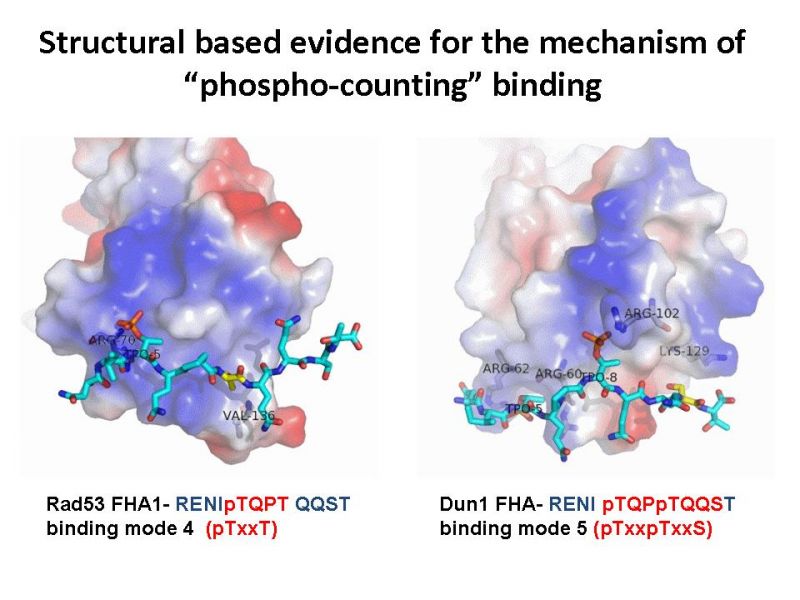
Novel mechanism for DNA damage signal transduction
Imbalance of tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes caused by gene mutations has been proven to directly contribute to tumorigenesis. The gene mutations occur due to fact that the DNA repair could not be fully completed during the cell cycle.
-
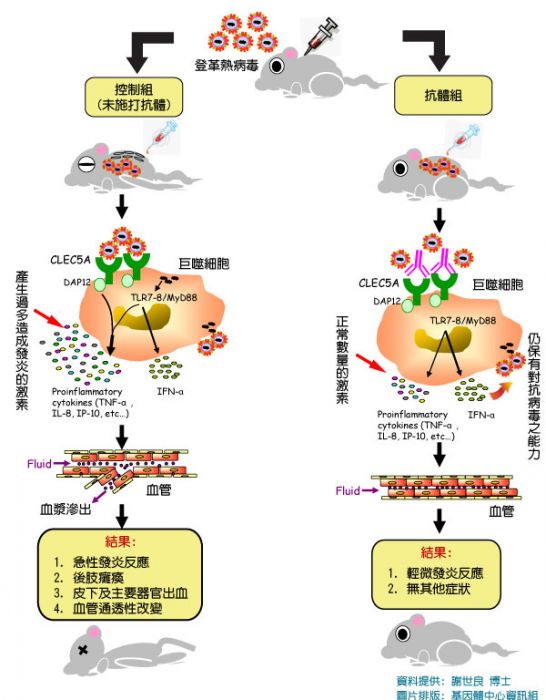
Collaborated Research Shed Lights on Potential Therapeutics for Dengue Fever
Dengue is mosquito borne and infects at least 50 million people a year and threatens two fifths of the overall population on earth. However, little was known about how the virus causes disease, not to say how to cure the infected.
-
Histone demethylase RBP2 finds its targets - Epigenetic Regulation in the focus!
Knowing all DNA sequences is enough to solve the mystery of the great diversity and complexity of life? Scientists have now put the idea aside since very little is different in DNA sequence between human and chimpanzees.
-
Discovery Of Antibiotics to Tackle the Problem of Drug Resistance
In the battle of mankind vs. bacteria, the first round was won by mankind due to the discovery of Penicillin. Antibiotics thus became a seemingly almighty weapon to some medical warriors.