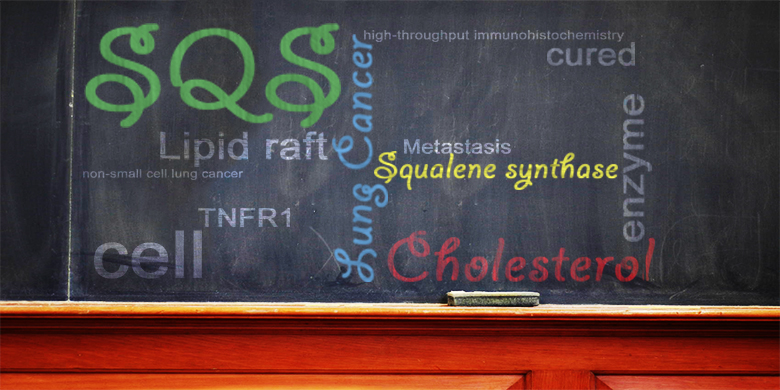News
-
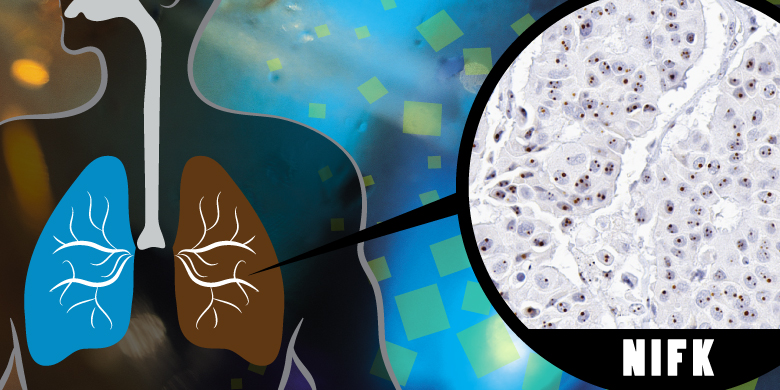
NIFK – What Causes Lung Cancer to Spread
After tissues are removed from cancer patients, pathologists’ role would start intensively giving patients a precise diagnosis and staging as the guide for cancer therapy. In some cancer types, the pathologist would use a biomarker named Ki-67 to tell how rapidly cancer cells divide and how vicious the tumor is. Tumors that produced more Ki-67 tend to grow faster and are more likely to link to poor disease outcome.
-
Glycan Technology - A New Chapter for Making Antibodies
The Glycomics focused research team in Genomics Research Center led by President Wong of Academia Sinica has been working on various glycan related subjects and successfully patented their inventions.
-
Antibody targeting IL-17B/RB proved effective for pancreatic cancer
Of all battles against cancer, when it comes to the therapeutics for pancreatic cancer, more than ever, it is too little and too late.
-
Cholesterol Synthesis Enzyme Proved Suspect in Lung Cancer Metastasis
Squalene synthase, commonly abbreviated as SQS, is an enzyme that has been shown to elevate cholesterol levels in mice when overly expressed.
-
Catch Me If You Can, I’m the Cancerous Brand
Circulating Tumor Cells, aka. CTCs is a research topic when scientists questioning when exactly cancer metastasis happens, and how we can find out in time when a few such run away cancer cells are floating inside patients’ blood.
-
The Mechanisms of Anti-IgE Medication in Treating Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, along with allergic rhinitis¸ allergic asthma, all can be considered diseases of affluence; that is because they happen much often in societies with increasing wealth and developments.
-
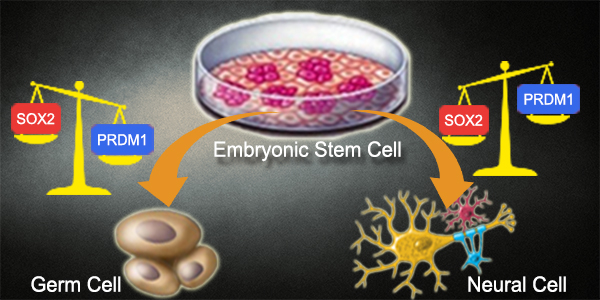
PRDM1/Blimp-1 Directs Germ Cell versus Neural Cell Pathway. During Early Human Embryonic Differentiation
In search for the root cause of human diseases related to gene deregulation has not been easy.
-
New Development of Universal Flu Vaccine
Throughout the year WHO Centers for Reference and Research on Influenza analyze virus isolates from patients around the world and made recommendation of which circulating influenza strains will be appropriate for seasonal vaccines. Still, with all these preventive measurements, influenza epidemics continue to be a threat to the public health.
-
When Lingzhi, B Cell and Globo H Meet
The lingzhi mushroom, or referred to as reishi mushroom in Japan, has been used as a medicinal mushroom in traditional Chinese medicine for more than 2,000 years, many believe it as a regulator to human immune system as well as its potential in treating cancers.
-
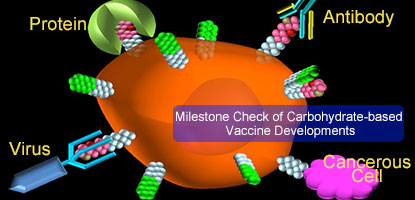
Milestone Check of Carbohydrate-based Vaccine Developments
For a decade of persevere investigation, the team focusing on carbohydrate-based vaccines development led by Dr. Chi-Huey Wong and Dr. Chung-Yi Wu has been publishing exciting progress reports periodically. Their work has a core scientific concept, which is, on the surfaces of most cancerous cells or the pathogen membrane, it is bound to find uncommon sugar molecules; as long as such a sugar molecular can be identified being uniquely associated with a particular disease, and there is a way to trigger the human immune system to respond to it and produce penetrating antibodies, then, by leveraging the nature’s way, vaccines can be built by mimicking the sugar molecule to let the body fight off the disease in a much more effective way.