News
-
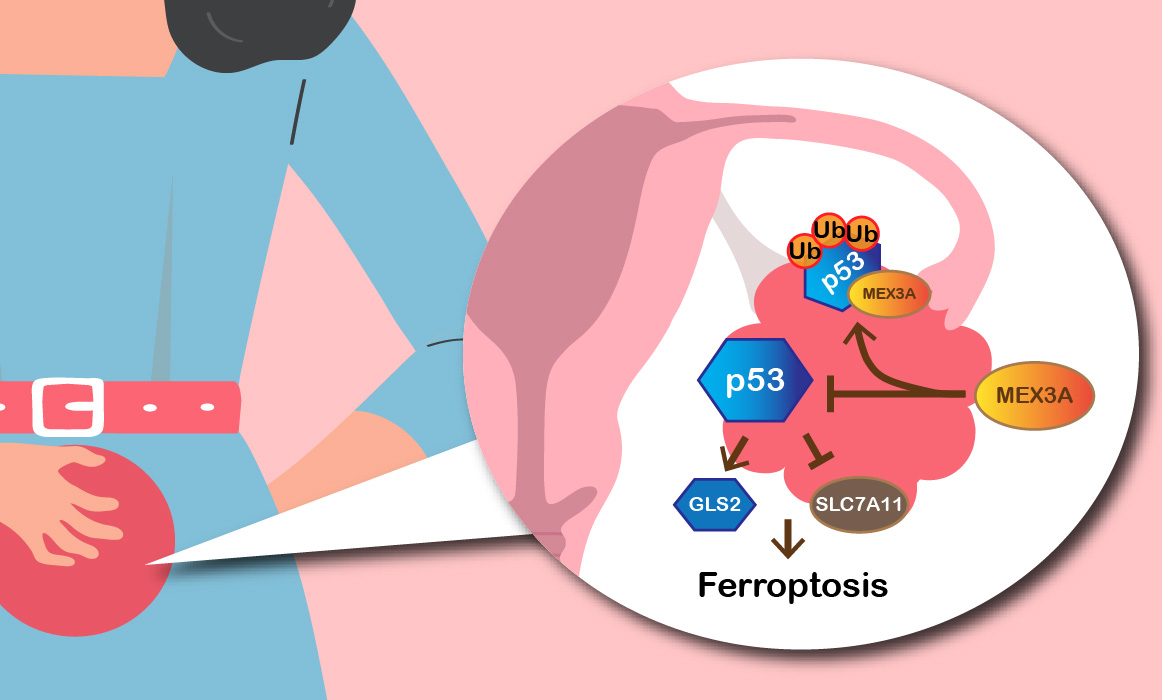
MEX3A mediates p53 degradation to suppress ferroptosis and facilitate ovarian cancer tumorigenesis
Among gynecological cancers, ovarian cancer (OC) has received less attention compared to breast cancer and cervical cancer.
-
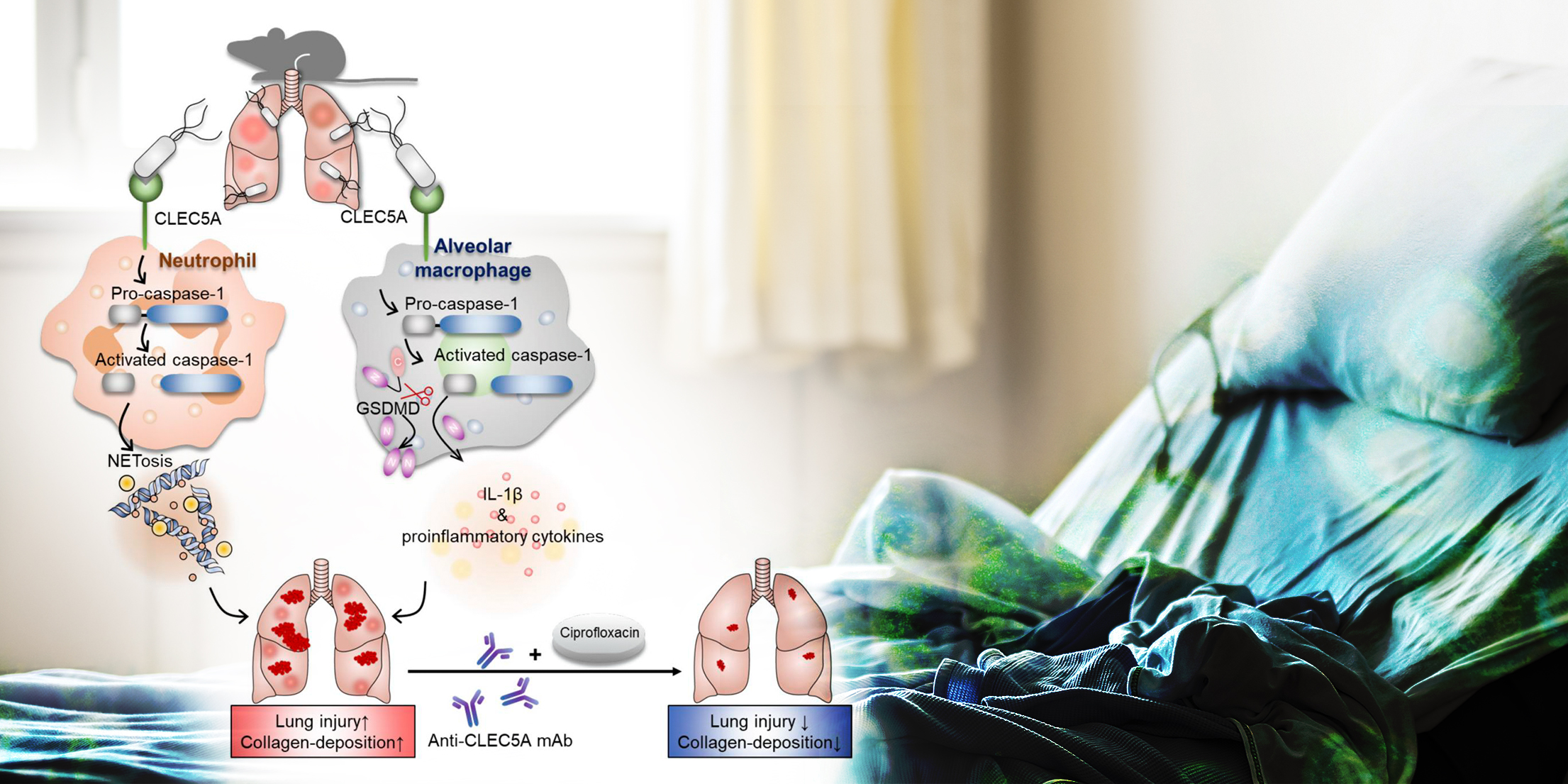
New direction for the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection combination of anti-CLEC5A monoclonal antibody with antibiotic
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the most common pathogens for nosocomial infections worldwide.
-
Role of hyperphosphorylation of TDP-43 in the neurodegenerative disease
A research team led by Dr. Yun-Ru (Ruby) Chen at Genomic Research Center, aims to study the misfolded proteins related to neurodegenerative diseases.
-
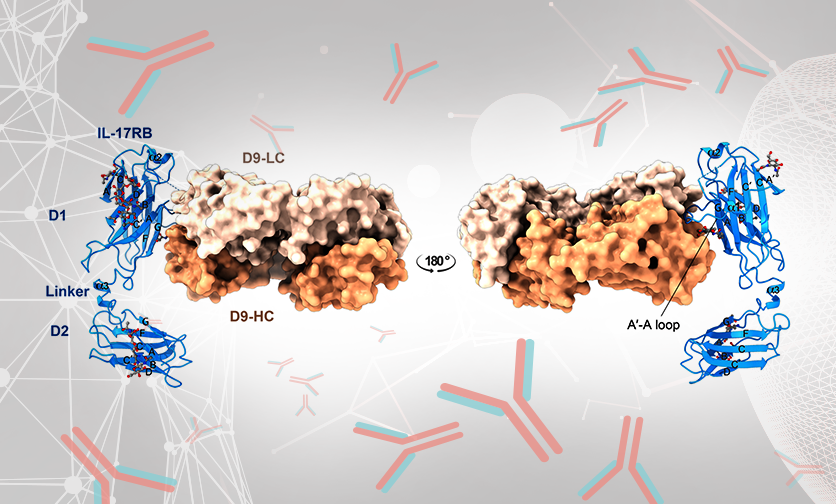
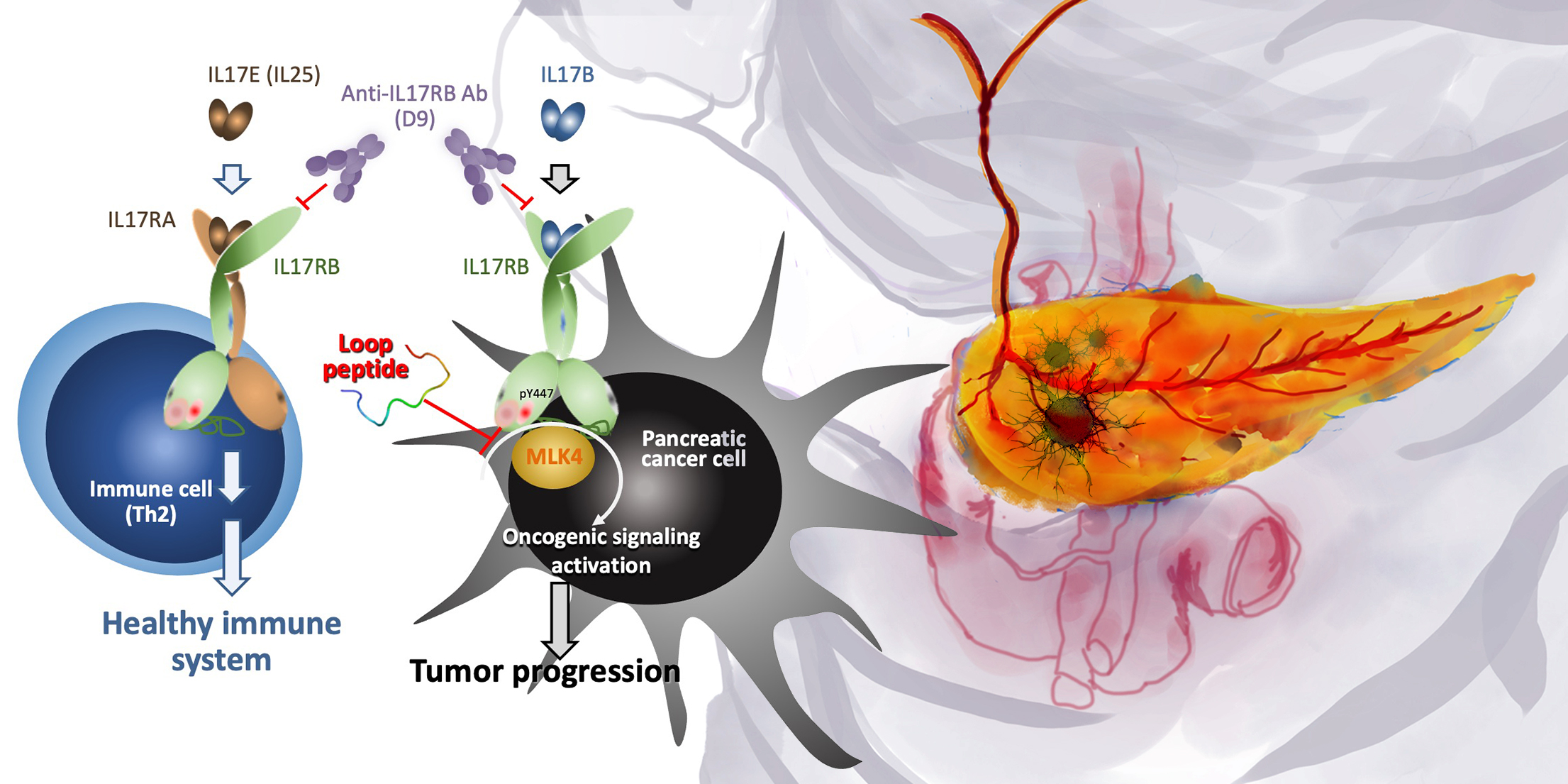
Crystal structure of 17B receptor complexed with antibody D9 provides solution for guiding antibody humanization and affinity maturation
A research team led by Dr. Che Ma and Dr. Wen-Hwa Lee in the Genomics Research Center reported they solved complex structure of IL-17RB with D9, and this structure provides important paratope information to guide the design of antibody humanization and affinity maturation of D9.
-
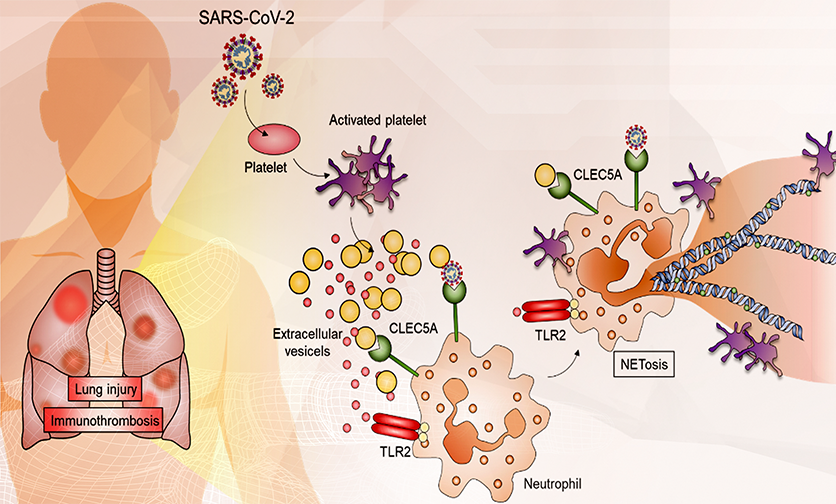
CLEC5A and TLR2 are critical in SARS-CoV-2 induced NET formation and lung inflammation
Coronavirus-induced disease 19 (COVID‑19) infects more than three hundred and sixty million patients worldwide, and people with severe symptoms frequently die of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
-
Chemists restructure an old natural product: Discovery a highly specific Golgi α-mannosidase inhibitor as a new anticancer agent
Glycoproteins play important roles in all kinds of biological events. Enzymes that were anticipated in modulation of N-glycosylation processes are regarded as a potential therapeutic target because of the key role they play in glycosylation processes. But some are undruggable because they belong to families of related enzymes that share the very similar active sites, and targeting them can lead to severe side effects.
-
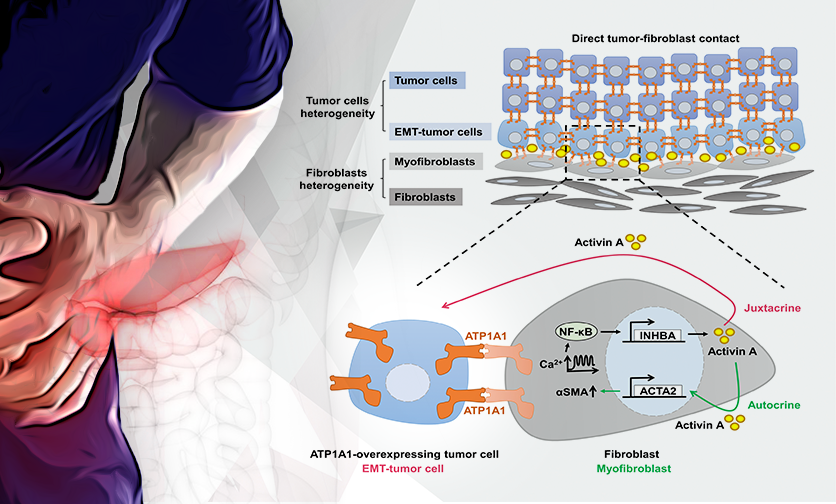
PDAC tumor cell-fibroblast interactions promote metastasis via Homophilic ATP1A1 Binding
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is responsible for more than 90% of pancreatic cancer cases, just 11% of PDAC patients live for at least five years after their diagnosis. It is seldom detected at its early stages when it's most curable.
-
Excess sugar intake increases the risk of pancreatic tumorigenesis
About 1.02 billion hand-shaken drinks are sold every year in Taiwan, working out to over 30% of people consume at least one cup a day. Excess sugar's impact on obesity and diabetes is well known. Still, one area that may surprise many men is consuming sugar in excessive amounts may contribute to the in-creased risk of Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
-
The critical point to treatment from the inside out: hybrid inorganic/organic nanoparticles with exosomes for cancer treatment
Since James E. Rothman, Randy W. Schekman, and Thomas C. Sudhof won the Nobel Prize in 2013 for revealing intracellular vesicles’ transport regulation mechanism, such as exosomes, which initially believed the primary function was only exosomes that transport cellular waste.
-
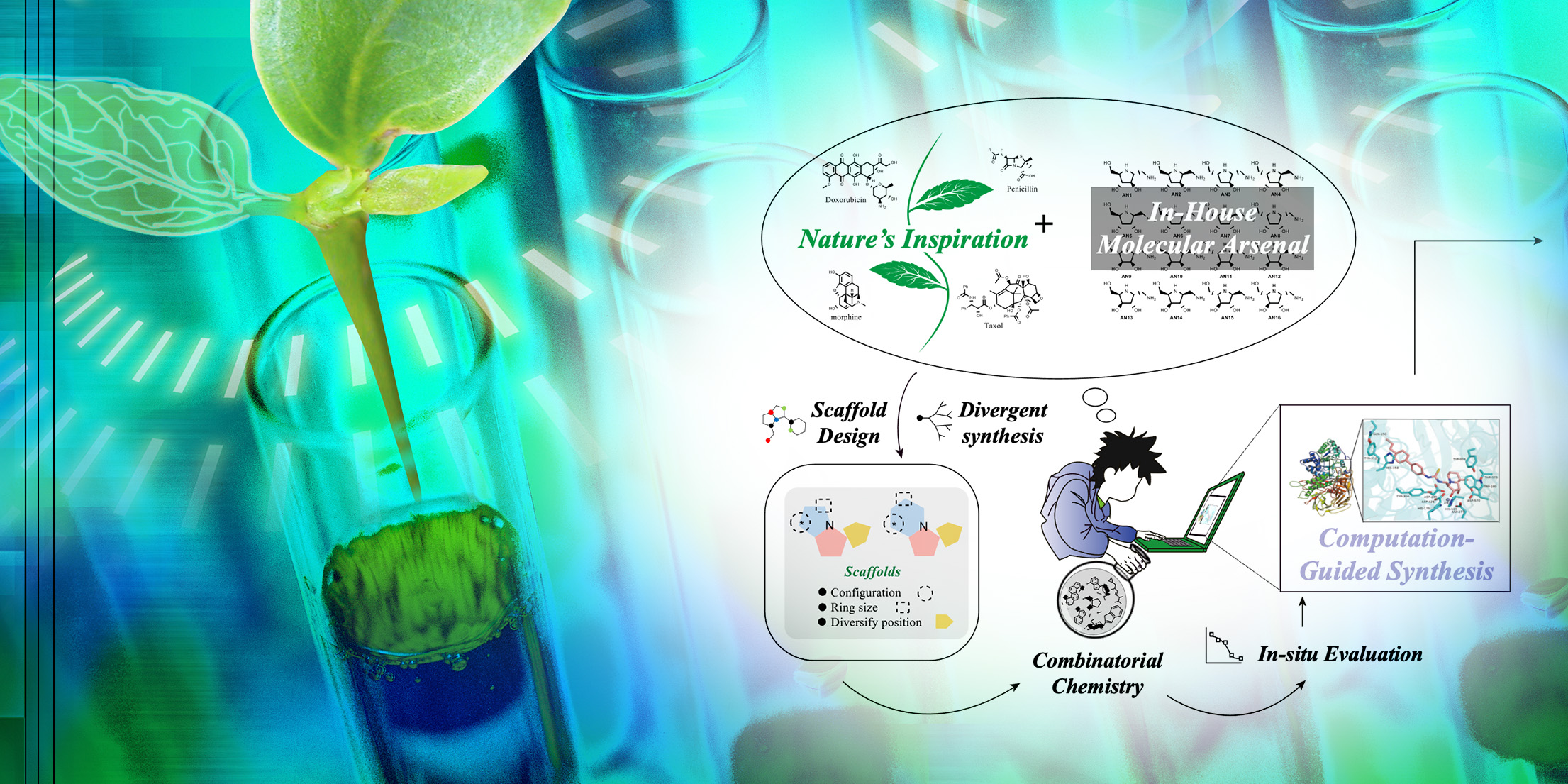
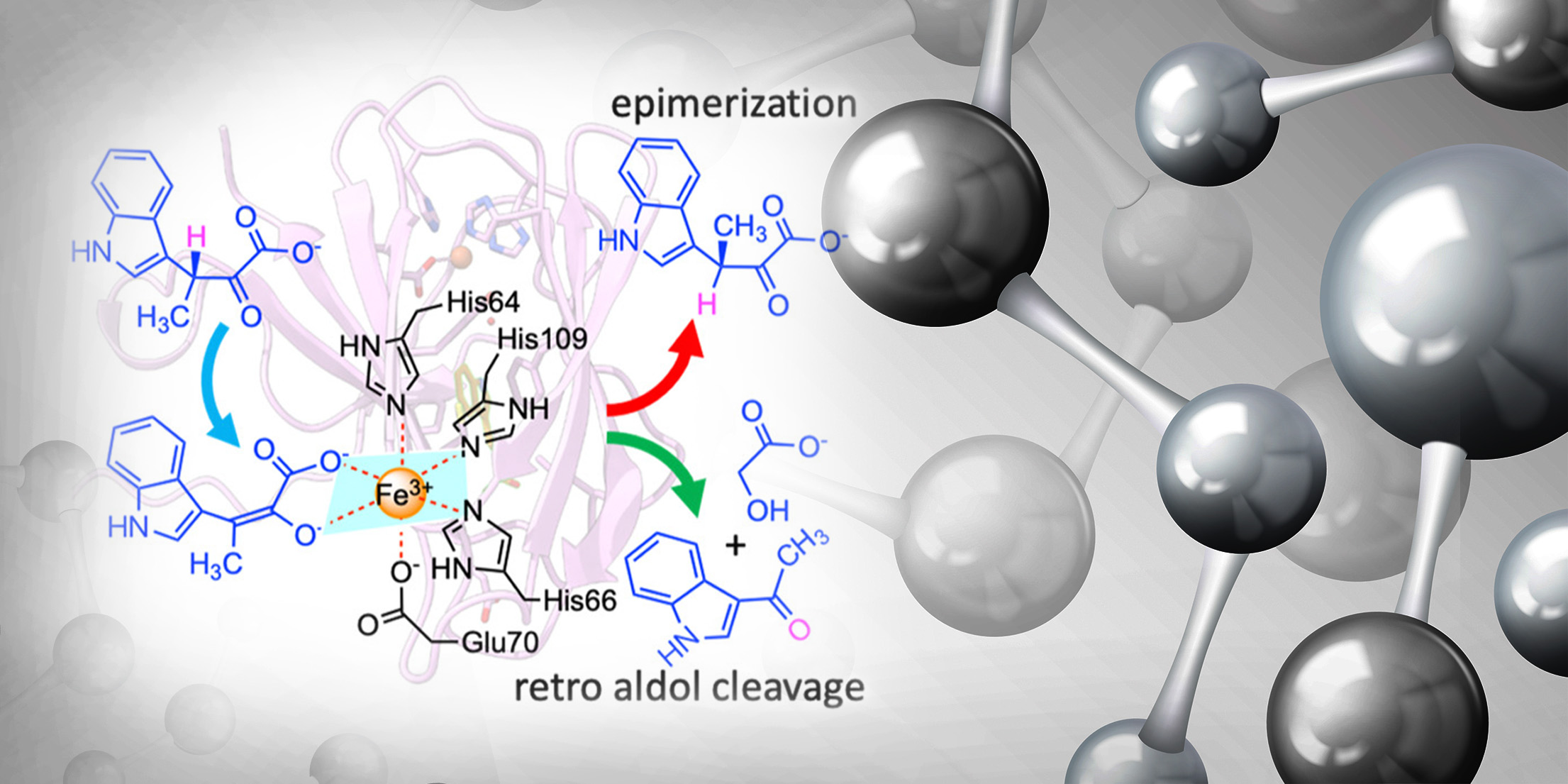
Learning from nature: StnK3 is the epimerase controlling β-methyl amino acid stereochemistry
Natural products are a significant source of structurally diverse bioactive compounds for pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food applications. Bioactive compounds often carry desired biological activities, such as anti-inflammation, anticancer, analgesics, and pain killing.
-
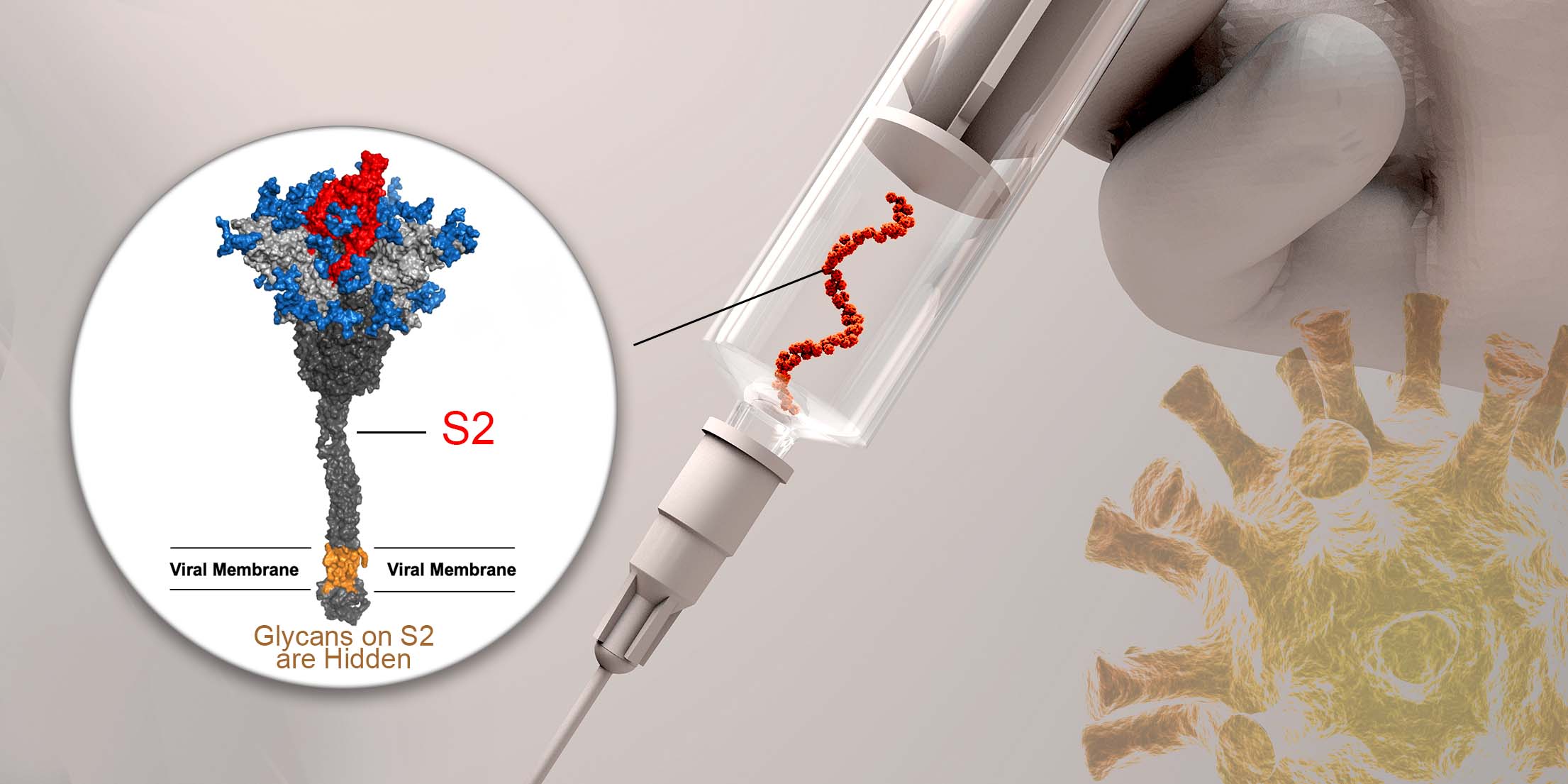
Mono-GlcNAc-decorated spike vaccine is highly effective against COVID-19 variants
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has resulted in more than 440 million confirmed cases and over 6 million deaths so far. Although there are COVID-19 vaccines available, viruses constantly change through mutations. Key questions remain about how quickly the variants can spread, their potential to evade immunity and how effective the vaccines are against the variants.
-
mRNA vaccine of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with deletion of multiple glycosites is broadly protective against variants of concern
Since the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) in December 2019 that caused Coronavirus Induced Disease 2019 (COVID-19), the virus has spread all over the world and caused more than 411 million infections and 5.8 million deaths in 25 months. Vaccination is an effective strategy to control the spread of SARS-CoV-2, and the protective antibodies induced by the vaccine are known to recognize the viral surface spike (S) protein and primed the T cell response. However, current vaccines may lose their efficacy because of the high mutation rate of SARS-CoV-2. To overcome this problem, development of a universal SARS-CoV-2 vaccine with broad protection against the current and upcoming variants is needed.
-
Dr. Chi-Huey Wong Honored as 2022 Recipient of the Tetrahedron Prize
Elsevier and the Board of Executive Editors of Elsevier’s Tetrahedron journal series has announced Academician Chi-Huey Wong as the recipient of the 2022 Tetrahedron Prize for Creativity in Organic Synthesis, in honor of his outstanding contributions in organic synthesis research. Dr. Wong is the first scholar from Taiwan to receive this award.
-
Novel MMT-based iron/platinum nanoparticles designed to enhance MRI contrast and HCC treatment
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays a pivotal role in the medical care of patients with or at risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Clinically, there exists about a 35% chance that contrast agents will be needed to improve the image sensitivity of MRI examinations. Commonly used products are iron-based contrast agents and gadolinium-based contrast agents.
-
Prof. Chi-Huey Wong ‒ First Glycoscientist Receives 2021 Welch Award in Chemistry
The Welch Foundation has announced that Academician Chi-Huey Wong, the Distinguished Research Fellow of Genomics Research Center, Academia Sinica has been awarded the 2021 Welch Award in Chemistry.
-
Activation of Prp28 ATPase at the Heart of Spliceosome for Spliceosomal Remodeling
Rubik’s Cube is one of the most popular 3D combinatorial games that captivates the world with its amazing complexity hidden behind the deceptively simplistic six bright colors. Remarkably, the most accomplished players can solve a completely scrambled Rubik’s Cube in less than twelve seconds. Few people, however, know that there is an equally complex Rubik’s Cube-like molecular machine in the cell. This machine is called “Spliceosome”, which must be sequentially remodeled or tweaked, just like the Rubik’s Cube, before it can be properly functioning in the gene expression pathway.
-
Anti-Siglec-3 mAb as immune checkpoint inhibitor to combat Hepatitis B infection
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a worldwide health problem. According to WHO’s report, there are over 257 million peoples globally infected by hepatitis B virus. HBV infection is prevalent in China, Taiwan, and Southeast Asia countries. Approximately 887,000 individuals die each year from HBV-related liver diseases or liver cancer.
-
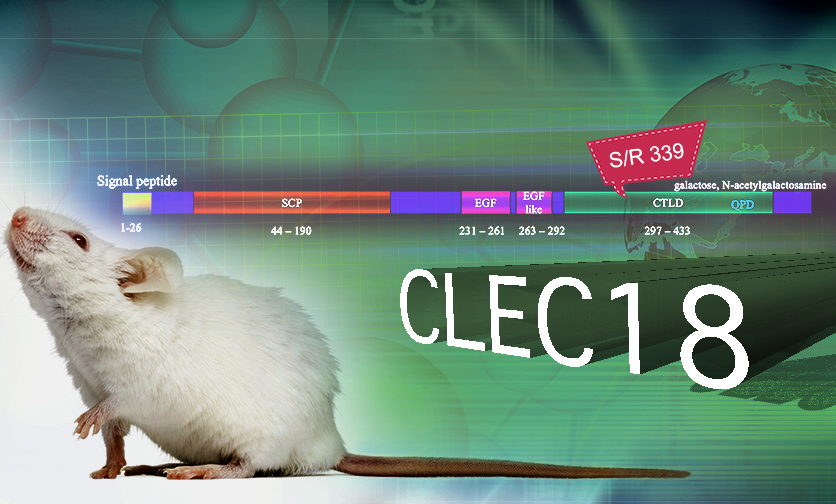
One Amino Acid Change Twice Immune Effect in CLEC18A to H5N1
CLEC18A is a member of C-type lectin family which is known to have influence over innate and adaptive antimicrobial immune responses, and its unknown biological mechanisms is to be unveiled.
-
Simplified Procedure to Prepare Remdesivir for SARS-CoV-2 and Nipah Virus
After grappling with the corona virus, SARS-CoV-2, for more than a year, the world is still being haunted by Covid-19. Remdesivir is the first drug approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat Covid-19. In May 2020, Taiwanese authority also approved the use of remdesivir in patients with severe COVID-19 symptoms.