Shang-Cheng Hung
Journal of the American Chemical Society
August 28, 2025
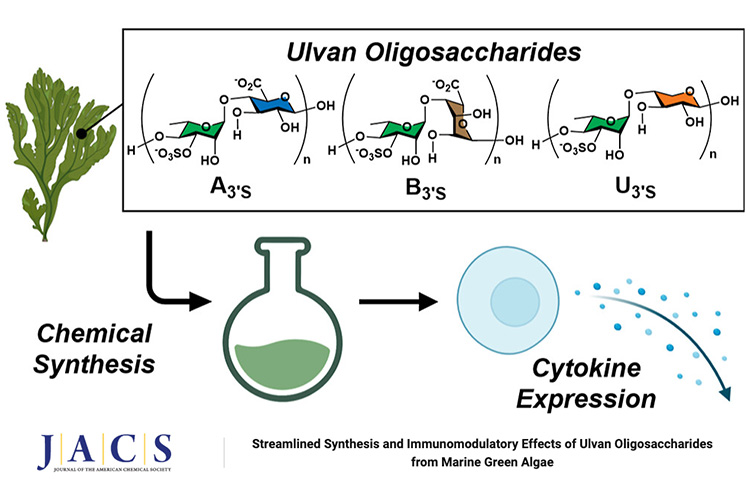
Green algae, commonly used as a source of food nutrients, contain ulvan, which is a water-soluble sulfated heteropolysaccharide isolated from Ulva. Ulvan exhibits a range of biological properties, including antitumor, antiviral, anticoagulant, and immunomodulatory activities. Its sugar backbone consists of 1→4-linked disaccharide repeating units, which are categorized as ulvanobiuronic acids (types A3′S and B3′S) and ulvanobioses (types U3′S and U2S3′S). Despite its promising therapeutic potential, the detailed structure–activity relationship of ulvan remains unclear. In this study, an efficient strategy was developed, utilizing orthogonally protected α1→4-linked l-Rha-d-Glc, l-Rha-l-Ido, and l-Rha-d-Xyl derivatives as disaccharide building blocks to synthesize di-, tetra-, hexa-, and octasaccharides of types A3′S, B3′S, and U3′S. The immunomodulatory effects of these compounds were evaluated through cytokine induction experiments. The results revealed that only the B3′S and U3′S octasaccharides had a significant influence on the gene expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, GM-CSF, and G-CSF. This chemical glycobiology approach offers valuable insights into the biomedical applications of marine ulvan oligosaccharides.


