 教授/國立臺灣大學醫學院內科
教授/國立臺灣大學醫學院內科
EDUCATION AND POSITIONS HELD:
- M.D., College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, 1979
- Ph.D., Graduate Institute of Clinical Medicine, National Taiwan University, 1990
- Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, 1993 – Present
- Research Fellow, Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica, 1993 – Present
- Associate Dean for Academic Affairs, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, 2001 – 2007
- Program Director, Microarray Core Facility, National Research Program for Genomic Medicine, 2002 – Present
- Director, Advisory Office, Ministry of Education, ROC, 2002 – 2005
- Dean, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, 2007 – Present
HONORS:
- Distinguished Teacher Award, National Taiwan University, 1999
- Academic Award, Ministry of Education, ROC, 2002
- Academician, Academia Sinica, 2006
- Distinguished Professor, National Taiwan University, 2006
- National Chair Professor, Ministry of Education, Taiwan ROC, 2007
- Academician ,The Academy of Sciences for the Developing World, 2008
RESEARCH INTERESTS:
 Our major research interests are lung cancer genomics, molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis and translational research related to personalized therapy of lung cancer. We have discovered novel genes and pathways that associated with lung cancer pathogenesis and progression. They also identified specific gene expression signature and microRNA signature that can predict the treatment outcome and may be useful for designation of personalized therapy for lung cancer patients.
Our major research interests are lung cancer genomics, molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis and translational research related to personalized therapy of lung cancer. We have discovered novel genes and pathways that associated with lung cancer pathogenesis and progression. They also identified specific gene expression signature and microRNA signature that can predict the treatment outcome and may be useful for designation of personalized therapy for lung cancer patients.
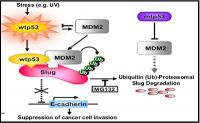
We recently identified that p53 can control cancer cell invasion and metastasis through the p53-MDM2-Slug pathway. The wild-type p53 (wtp53) forms a wtp53-MDM2-Slug complex that induces Slug degradation, thereby suppresses cancer cell invasion. In contrast, mutant p53 (mtp53) inactivates Slug degradation and increases cancer cell invasion.